Model Forests are social, inclusive and participatory processes that seek the sustainable development of a territory and thus contribute to global targets related to poverty, climate change, desertification and sustainable development. More than 31 million hectares in 15 countries in Latin America are part of the 30 Model Forests in this region.
The Ibero-American Model Forests reflect a mosaic of uses and ownership, where the livelihoods of its people combine various activities ranging from agriculture, livestock, forestry, tourism and conservation.
Stakeholders seek to advance sustainable land management in a collaborative and coordinated wayoften creating local leadership strategies to coordinate activities related to protected areas, biological corridors, forest management, sustainable agriculture, rural tourism, access to microcredit, organic farming, watershed management and forest certification.
Principles and AttributesThe Model Forests around the world are as unique and diverse as the countries and cultures in which they are located. Although Model forests participants define together their own priorities and governance structure, at a global scale they are connected by common attributes. Every Model Forest shares a core of six principles that provide coherence to the IMFN and the basis for networking and knowledge sharing. Principle 1. Broad-base Partnership Principle 2. Large Landscape Principle 3. Commitment to Sustainability Principle 4. Participatory Governance Principle 5. A Broad Program of Activities Principle 6. Commitment to Knowledge Sharing, Capacity Building and Networking Criteria and IndicatorsThe above six principles have been broken down in 23 criteria and 68 indicators for monitoring and evaluation purposes. See the Criteria and Indicators: Spanish – Portuguese – English Download the Standard for the Monitoring and Evaluation of Model Forests (in Spanish only)
CATIE/RIABM, 2012.
|

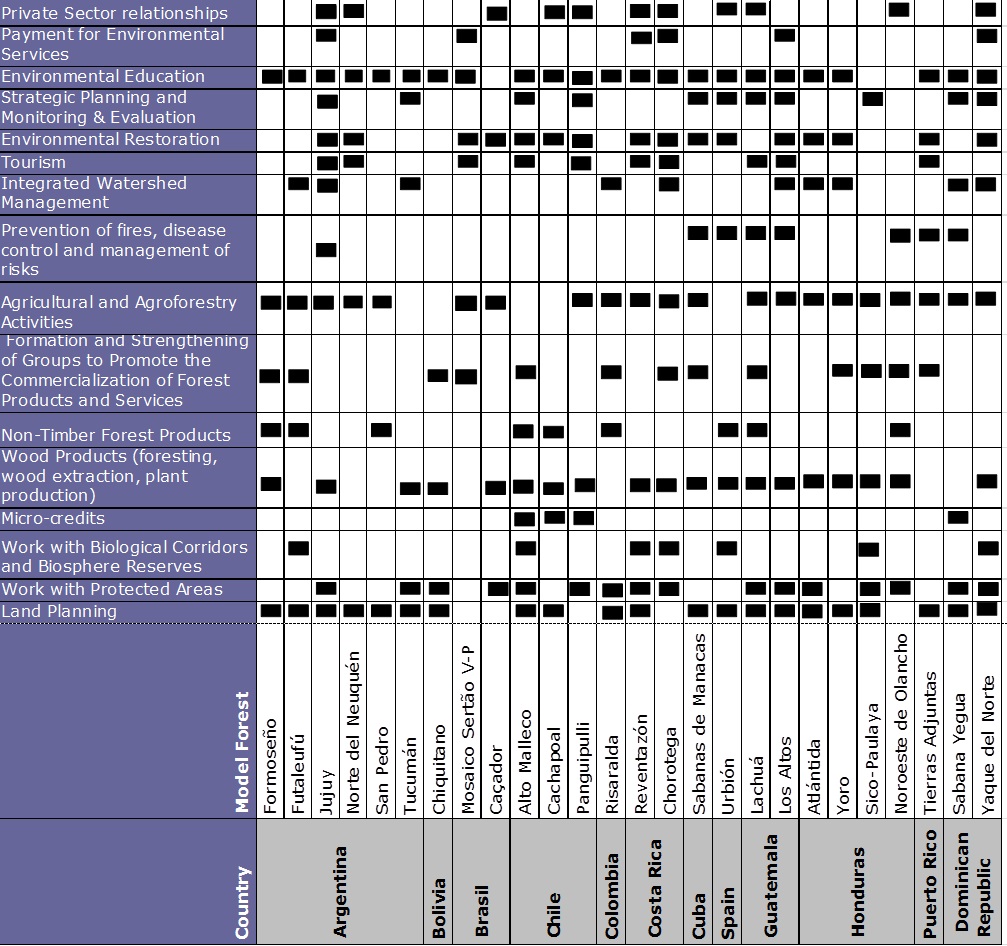
 Proposal to Guide the Management of the Ibero-American Model Forest Network Initiatives
Proposal to Guide the Management of the Ibero-American Model Forest Network Initiatives

